- Published on
Automating EC2 Spot Interruption Handling with Karpenter and Terraform
- Authors

- Name
- Sneha Tuladhar
- @
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Architecture Overview
- Step-by-Step Implementation
- Best Practices for Implementation
- Key Terraform Considerations
- Conclusion
Introduction
Amazon EC2 Spot Instances provide significant cost savings of up to 90% compared to On-Demand instances but come with the trade-off of potential interruptions—often with just a two-minute warning.
To ensure workloads remain resilient, Karpenter, a flexible Kubernetes node provisioning system, integrates with Amazon SQS to process interruption events delivered from Amazon EventBridge.
This setup allows Karpenter to automatically detect termination notices, drain affected nodes, and provision replacements. By configuring an SQS queue with EventBridge and linking it to Karpenter, organizations can seamlessly reschedule workloads with minimal disruption while continuing to maximize the cost benefits of Spot Instances.
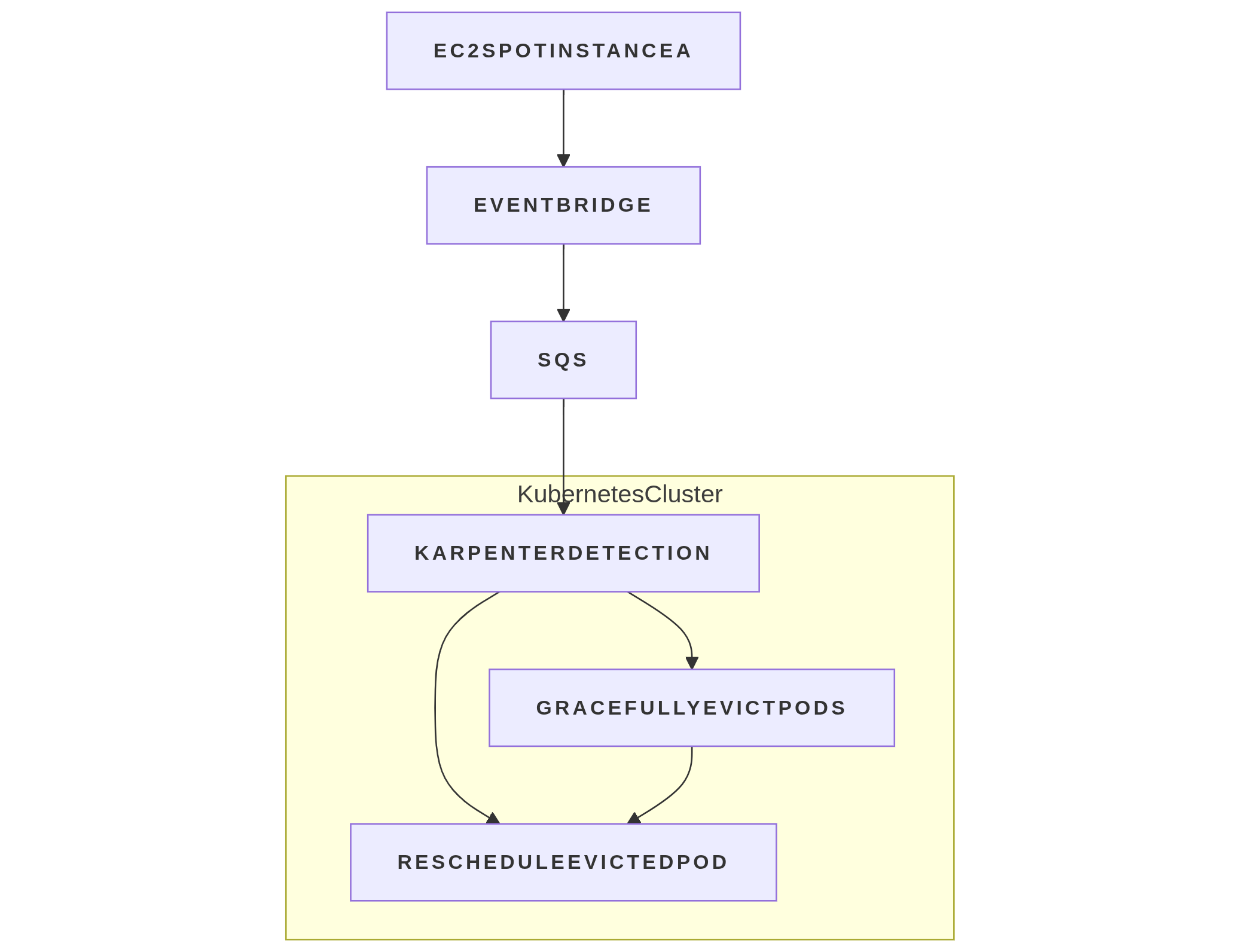
Architecture Overview
The Terraform configuration provisions the following components:
- SQS Queue — Acts as a buffer for interruption events
- EventBridge Rules — Capture EC2 Spot Interruption Warnings and Rebalance Recommendations
- IAM Policies — Grant Karpenter permissions to access SQS and EventBridge to send events
- Terraform Modules — Modularized setup for maintainability
Step-by-Step Implementation
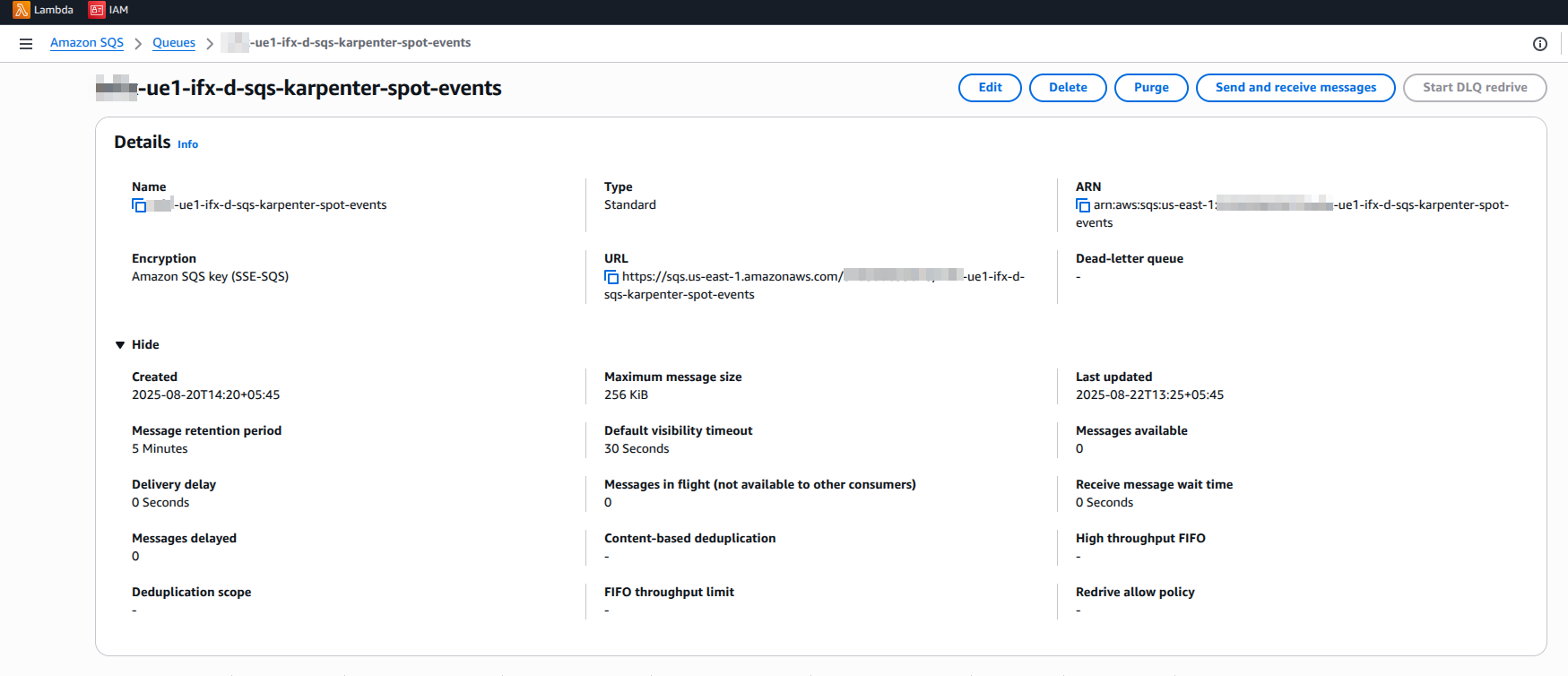
Step 1: SQS Queue Configuration
The SQS queue is configured with:
- Message Retention:
1209600seconds (14 days) to ensure messages are retained during processing delays - SSE Enabled: Server-side encryption for security
- Visibility Timeout:
300seconds (5 minutes), allowing sufficient time for Karpenter to process messages - Delay Seconds:
0to ensure immediate message delivery
Terraform snippet:
module "karpenter_interruption_sqs" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/sqs/aws"
version = "4.2.1"
name = "${module.naming.resources.sqs.name}-karpenter-spot-events"
message_retention_seconds = 1209600
visibility_timeout_seconds = 300
delay_seconds = 0
sqs_managed_sse_enabled = true
tags = {
"karpenter.sh/discovery" = module.eks.cluster_name
}
}
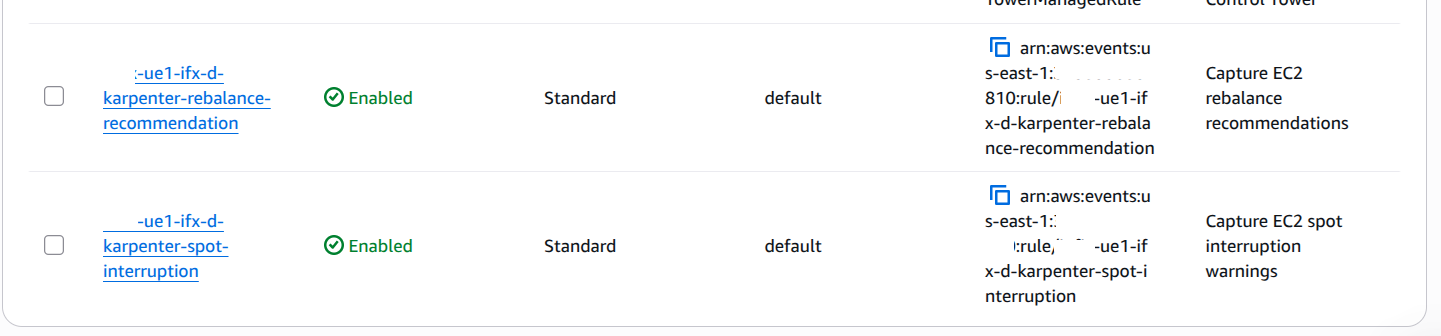
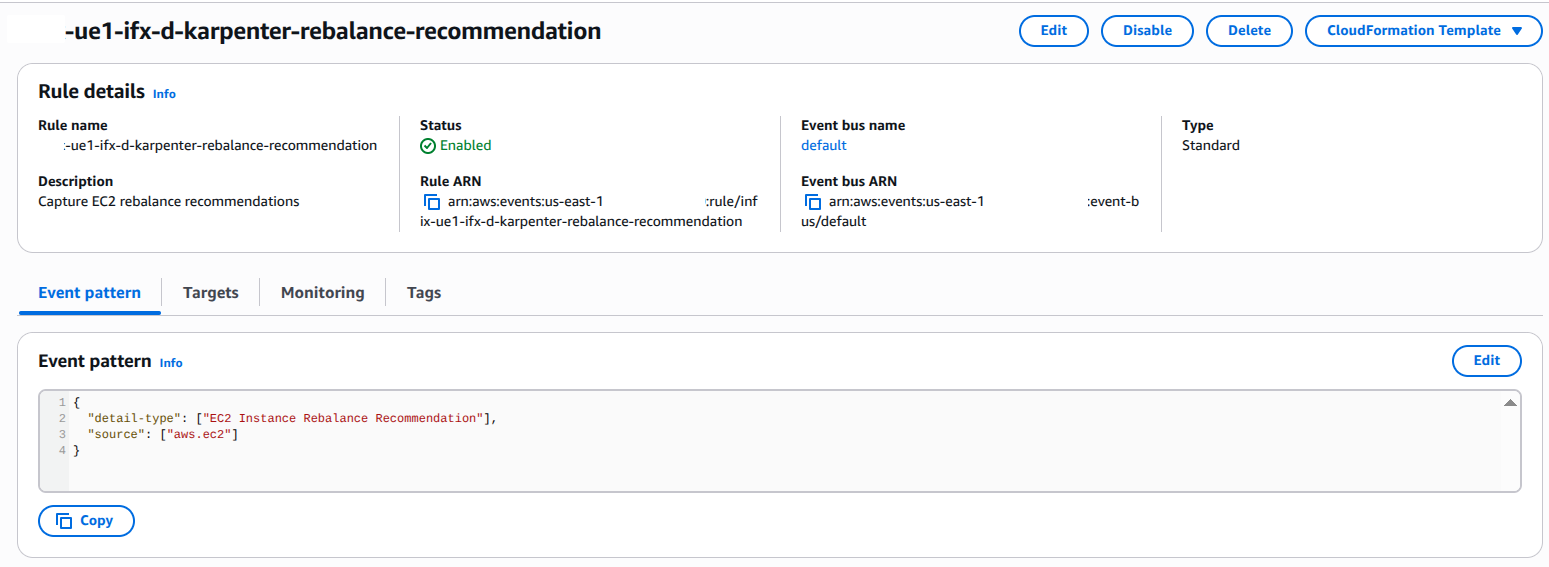
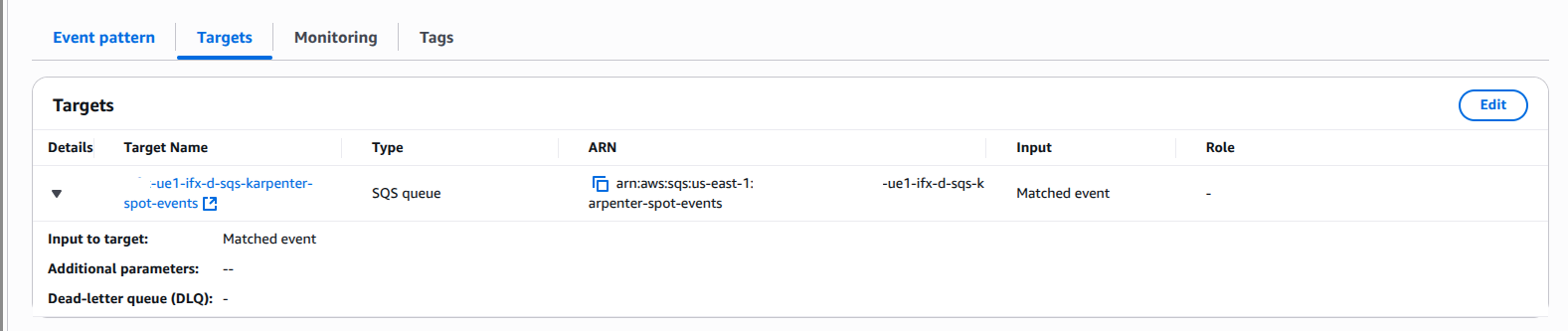
Step 2: Configure EventBridge Rules
EventBridge captures Spot Interruption Warnings and Rebalance Recommendations, which are then sent to SQS.Two EventBridge rules capture:
- Spot Interruption Warnings: emitted two minutes before EC2 reclaims capacity
- Rebalance Recommendations: notifications when EC2 recommends replacing Spot Instances for better availability .
Terraform snippet: Event Pattern Example
{
"source": ["aws.ec2"],
"detail-type": ["EC2 Spot Instance Interruption Warning"]
}
Terraform Code: Terraform snippet:
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_rule" "spot_interruption_rule" {
name = "${module.naming.resources.prefix.name}-karpenter-spot-interruption"
description = "Capture EC2 spot interruption warnings"
event_pattern = <<PATTERN
{
"source": ["aws.ec2"],
"detail-type": ["EC2 Spot Instance Interruption Warning"]
}
PATTERN
}
Step 3: Define IAM Policies for SQS Access
Karpenter requires permissions to interact with the SQS queue:
- SendMessage, ReceiveMessage, DeleteMessage — Manage queue messages.
- GetQueueAttributes, GetQueueUrl — Retrieve queue details.
- ListQueues — Discover available queues.
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "karpenter_sqs_policy" {
statement {
effect = "Allow"
actions = [
"sqs:SendMessage",
"sqs:ReceiveMessage",
"sqs:DeleteMessage",
"sqs:GetQueueAttributes",
"sqs:GetQueueUrl"
]
resources = [module.karpenter_interruption_sqs.queue_arn]
}
statement {
effect = "Allow"
actions = ["sqs:ListQueues"]
resources = ["*"]
}
}
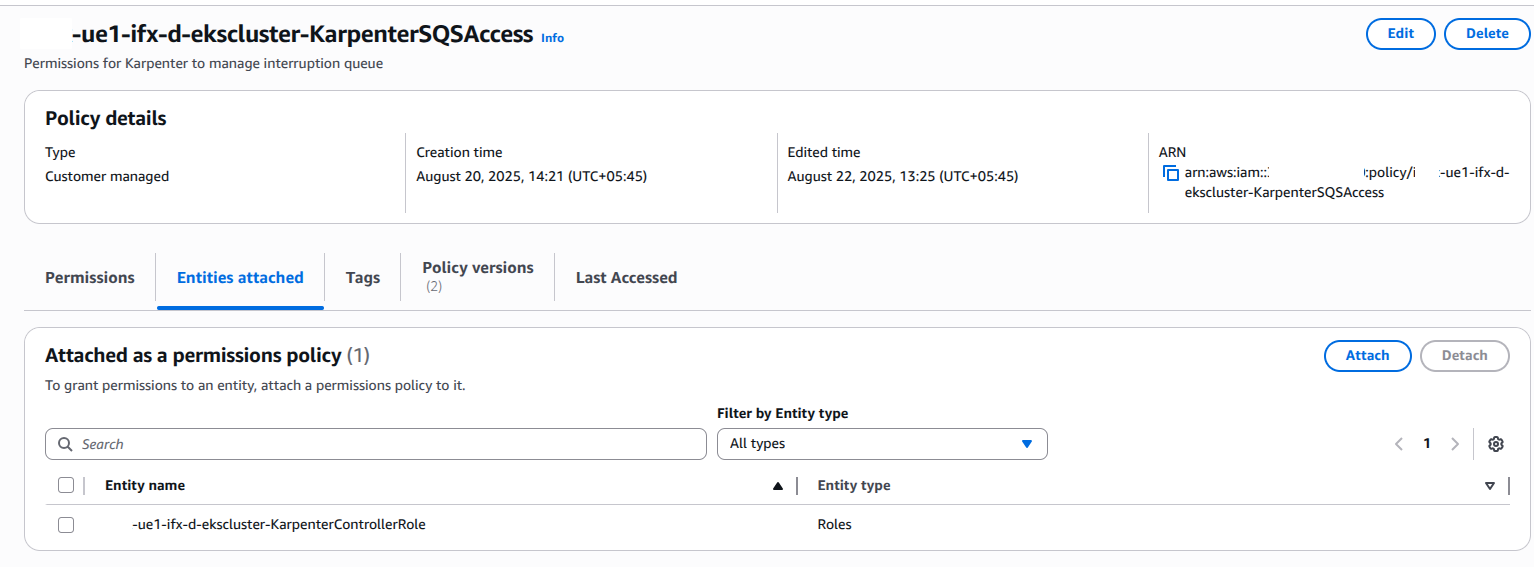
Step 4: Granting Karpenter Access to the SQS Interruption Queue
To allow Karpenter to respond to Spot Instance interruption notices, we need to grant its Controller role permissions to interact with the SQS queue.
Attach the IAM policy to the Karpenter Controller role:
# Grant Karpenter Controller access to SQS
resource "aws_iam_policy" "karpenter_sqs_access" {
name = "${module.eks.cluster_name}-KarpenterSQSAccess"
description = "Permissions for Karpenter to manage interruption queue"
policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.karpenter_sqs_policy.json
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "karpenter_sqs" {
role = aws_iam_role.karpenter_controller.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.karpenter_sqs_access.arn
}
Step 5: Allow EventBridge to Send Messages to SQS
To enable EventBridge to deliver interruption events to the SQS queue, attach a queue policy as shown below:
resource "aws_sqs_queue_policy" "karpenter_interruption_policy" {
queue_url = module.karpenter_interruption_sqs.queue_url
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [{
Effect = "Allow",
Principal = { Service = "events.amazonaws.com" },
Action = "sqs:SendMessage",
Resource = module.karpenter_interruption_sqs.queue_arn,
Condition = {
ArnEquals = {
"aws:SourceArn" = [
aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.spot_interruption_rule.arn,
aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.rebalance_recommendation_rule.arn
]
}
}
}]
})
}
Step 6: Configure Karpenter
Enable interruption handling by pointing Karpenter to the SQS queue using the --interruption-queue flag.
⚠️ Note: Avoid conflicts with other Node Termination Handlers that might also manage Spot interruptions.
Best Practices for Implementation
- Tagging: Add
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${cluster_name}to the SQS queue to allow Karpenter to discover it. - Error Handling: Configure a Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) for failed message processing to avoid losing events.
- Cross-Account: Ensure IAM roles and resource policies are correctly set if using multiple AWS accounts.
Key Terraform Considerations
- Modularization: Use Terraform modules to maintain consistency and simplify updates.
- Dependency Management: Ensure the SQS queue is created before EventBridge rules and IAM policies to prevent Terraform errors.
- Outputs: Expose the SQS queue ARN and URL as outputs for easy integration with Karpenter Helm charts.
Conclusion
By implementing this SQS and EventBridge integration, Karpenter can proactively replace interrupted Spot nodes, ensuring workloads remain resilient while optimizing costs.
This Terraform-based setup provides a production-ready foundation aligned with AWS best practices, allowing organizations to:
- Efficiently manage Spot Instance interruptions without manual intervention
- Automate, scale, and cost-optimize Kubernetes node management
- Reduce operational overhead and improve overall cluster reliability